muscle fiber orientation
Birman V Genin G. We employed a whole body magnetic resonance imaging protocol to examine the influence of age gender body weight and height on skeletal muscle SM mass and distribution in a large and heterogeneous sample of 468 men and women.

This Diagram Shows The Different Ways Receptors Are Classified By Modality Modality Is The Type Of Stimulus That Is Used
The anterior oblique subsystem also functions in a transverse plane orientation very similarly to the posterior oblique subsystem only from the anterior portion of the body.

. The third layer is the popular transverse abdominus muscle. To learn about muscle synergies and local and global mobility muscles. Qazi et al 2015.
Interconnection and orientation as a function of muscle length and activity. Citation neededAromatic in the name refers to the presence of aromatic rings of six carbon atoms. 107 Smooth Muscle Tissue.
However their efficiency is low. Capillaries are often seen as the source of oxygen for the mitochondria in. Cardiac muscle encompasses the heart which keeps the human body alive.
Smooth muscle is present. Prone describes a face-down orientation and supine describes a face up orientation. Arrangement of Fascicles.
Men had significantly P 0001 more SM in comparison to women in both absolute terms 330 vs. Internal means inside and oblique comes from the Latin word obliquus which means a slanting orientation. Thermally activated coiled polymer fiber actuators 499 kWkg and shape-memory alloys 50 kWkg 11 26 have higher peak specific power.
These terms are sometimes used in describing the position. Force production and gearing vary depending on the different muscle parameters such as muscle length fiber length pennation angle and the. The skeletal muscle extracellular matrix ECM plays an important role in muscle fiber force transmission maintenance and repair.
Parallel pennate and hydrostats. Relationship between capillary supply and size of a muscle fiber. Collagen fiber orientation at the tendon to bone insertion and its influence on stress concentrations.
ATP hydrolysis causes the myosin heads to swivel and change orientation. Micro and Nanolignin in Aqueous Dispersions and Polymers 2022. Generally improved CF properties are attributed to a high degree of carbon orientation and cross-linking as well as the elimination of pores and heterogeneities in the graphitic structure of the fiber.
Aramid is a shortened form of aromatic polyamideThe term was introduced in 1972 accepted in 1974 by the Federal Trade Commission of the USA as the name of a generic category of fiber distinct from nylon and adopted by the International Standards Organisation in 1977. Journal of Biomechanics 2006. Yusuf and Brand-Saberi 2012CF may be compromised during aging or due to major injuries or genetic.
What do the names of the external and internal oblique muscles mean. Operating under a poorly understood. 105 Types of Muscle Fibers.
106 Exercise and Muscle Performance. The fiber arrangements of these muscles run perpendicular to the sacroiliac joint SIJ. Skeletal cardiac and smooth muscle.
210 kg and relative to. Wang et al 2019. There arethree major muscle types found in the human body.
Shadrin et al 2016 which is necessary for locomotion respiration and metabolic processes Kaji et al 2010. Slide 059-3 forearm muscle Masson cross fetal View Virtual Slide. There are several different muscle architecture types including.
103 Muscle Fiber Excitation Contraction and Relaxation. In both injured and diseased states ECM adapts dramatically a property thathas clinical manifestations and alters muscle function. In this animation the myosin head is attached to actin when ATP hydrolysis causes it to swivel In reality the myosin head swivels when unattached and then returns to its.
The tibialis anterior muscle has a complex orientation of muscle fibers and the mechanical strain on muscle fibers both in the relaxed and activated strain may vary along to the superficialdeep axis. All skeletal muscle is made up of fascicles bundles of fiber but fascicle arrangements vary considerably resulting in muscles with different shapes and functional capabilities. Each muscle has two tendons one proximally and one distally.
The measured peak specific power is double that of natural muscle and comparable to values for silicone DE actuators. Muscle fiber and muscle cell are synonymous. The main function of skeletal muscle is to produce contractile force CF Vandenburgh et al 2008.
The most common patterns of fascicle arrangement are circular parallel convergent and pennate. This browser cannot play the embedded video file. Each muscle type has unique cellular components physiology specific functions and pathology.
The orientation of fibers influences the overall function of the muscle. Muscle fiber growth is accomplished by means of a population of myogenic cells called satellite cells which take up positions between the muscle fiber and the basal lamina in which each muscle fiber encases itself see Figure 2. The point at which the tendon forms attachment to the muscle is also known as the myotendinous junction.
Skeletal muscle is an organ that primarily controls movement and posture. Groups of individual cells that are surrounded by perimysium are known as fascicles and groups of these fascicles surrounded by epimysium make up a muscle. Muscle architecture is the physical arrangement of muscle fibers at the macroscopic level that determines a muscles mechanical function.
104 Nervous System Control of Muscle Tension. So the name internal obliques refers to the location and shape of the muscle.

Skeletal Muscle Shapes Within The Body Human Muscle Anatomy Body Muscle Anatomy Types Of Muscles

Cross Section Of A Muscle Fibre Gummy Candy Peach Rings Sketch Book

The Thoracolumbar Spine Joint Spines Thoracic

Langers Lines Lines Of Dominant Mechanical Tension In The Skin General Practice Notebook Acupressure Treatment Skin Medical Dictionary

Study Biology Anatomy And Physiology Biology

The Spiral Engine Of Locomotion Anatomia Anatomia Musculos Anatomia Medica
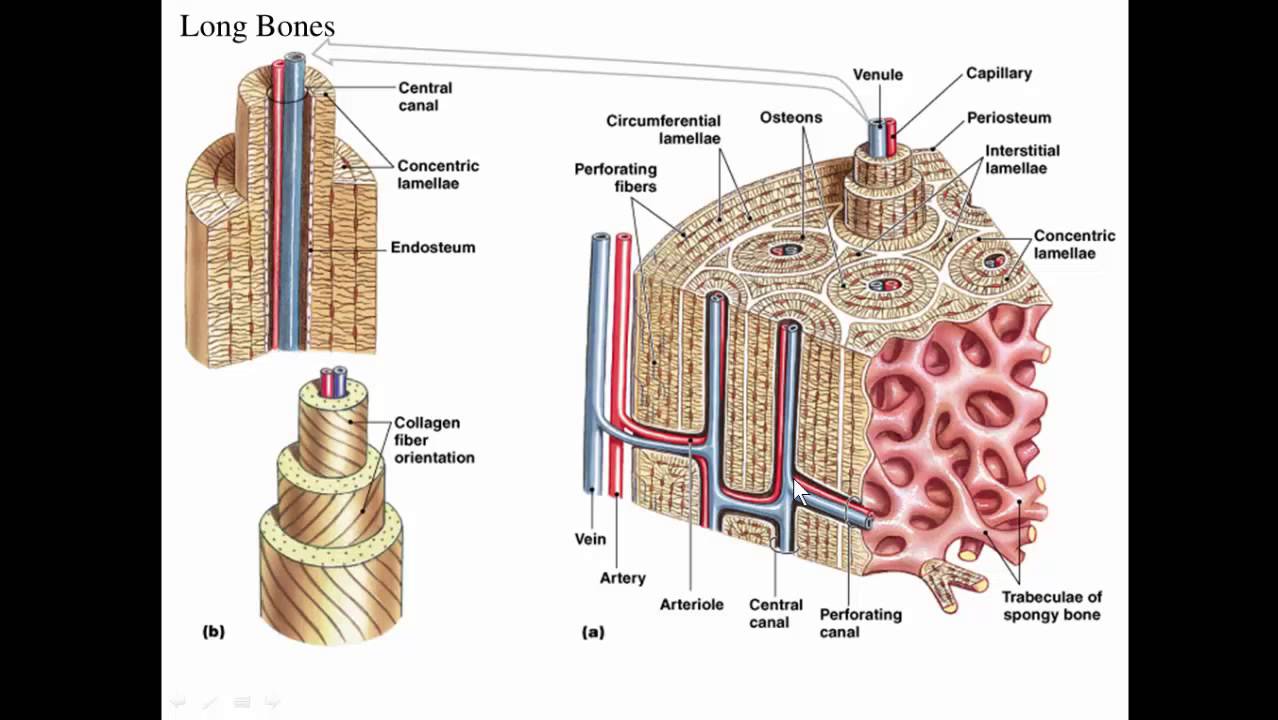
Long Bone Compact Bone And Spongy Bone Anatomy Bones Human Anatomy Anatomy

Actin And Myosin Interaction Produces Tension Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Muscle System

Myotonic Dystrophy Ring Fibres Hyaline Fibres Dmd Myotonic Dystrophy Fiber Stain

Tension Production By Muscle Fibers Sarcomere Length Anatomy And Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Muscle System









Comments
Post a Comment